POWER PLANTS
Fire & Gas Detection for Turbines, Boilers, Fuel Systems & Electrical Infrastructure
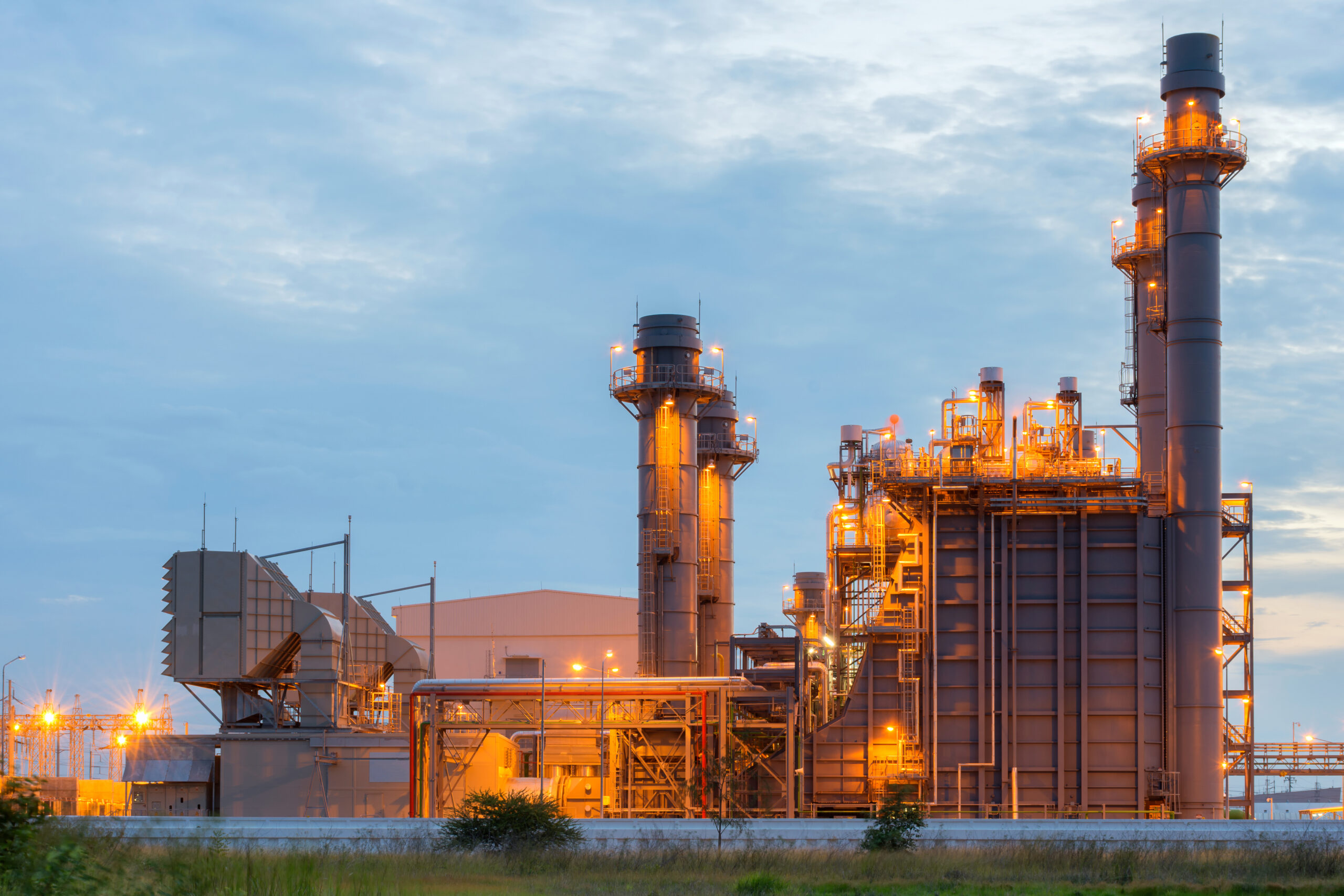
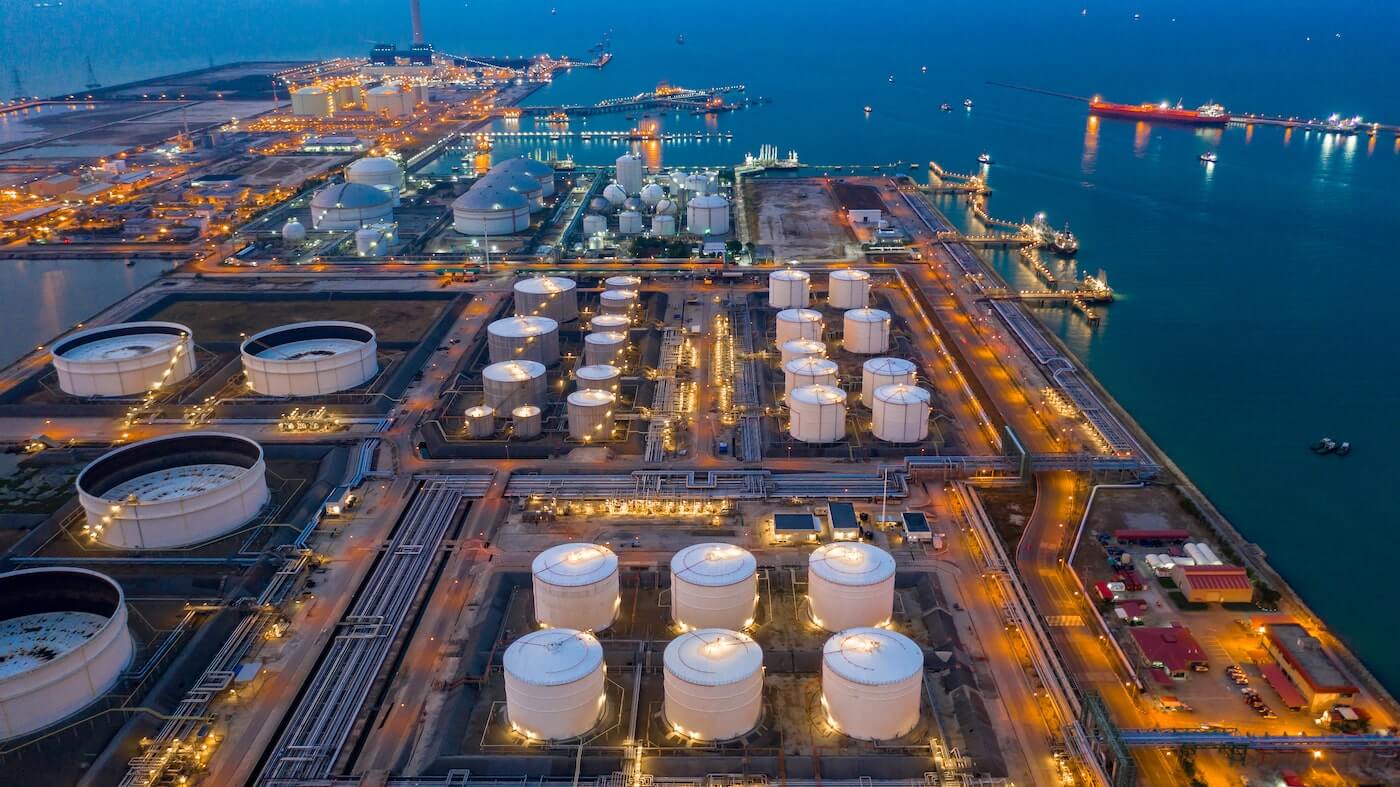
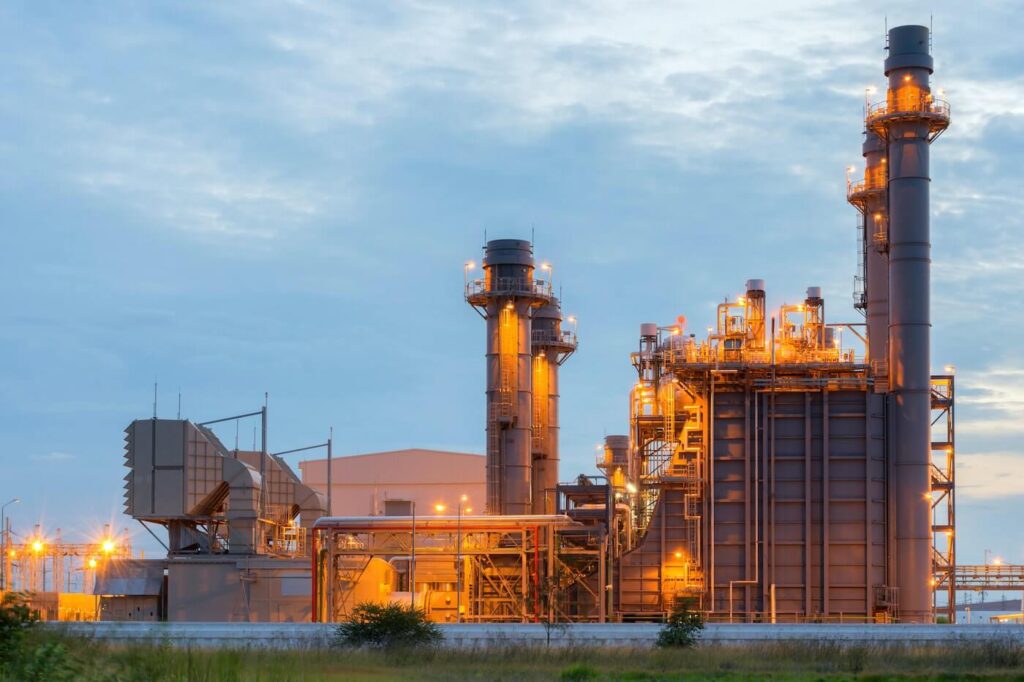
Power plants operate some of the most critical and high-energy equipment in the industrial world. Steam turbines, gas turbines, generators, boilers, fuel-handling systems, and high-voltage equipment work continuously under heat, pressure, and mechanical load.
Up to $5 million
typical financial loss caused by a single fire-related turbine shutdown.
>45%
of power-facility fires begin in electrical systems or cable areas.

High-energy operations demand dependable detection
Power generation relies on controlled combustion, high-temperature process equipment, and a constant flow of fuel or steam. Even small failures — such as overheating bearings, insulation breakdown, lubrication leaks, or electrical faults — can turn into ignition sources.
Because power plants operate with 24/7 uptime requirements, any incident can lead to major production losses and grid instability. Early detection is a critical layer of protection that helps prevent escalation in areas where fires can spread quickly through cable trays, turbine housings, boiler sections, or fuel systems.
Detection technology designed for power-plant conditions
Omniguard detection products are engineered for environments characterized by heat, vibration, airflow, and electrical interference. Our flame detectors respond quickly to turbine, boiler, burner, and fuel-area ignition events — even in bright or reflective surroundings.
Gas detectors identify fuel leaks early, especially around gas turbines, burners, pipe connections, and fuel-delivery systems. Smoke detection supports protection inside cable tunnels, electrical rooms, control areas, and auxiliary equipment spaces.
Our detection products support:
- Fast response time and long detection distance
- Wide viewing angles
- Designed for easy cleaning and maintenance
- All models are available with Aluminum or Stainless-Steel housing
- Worldwide service and support network
Typical ignition scenarios in power-generation environments
Incidents in power plants often originate in enclosed or hard-to-reach locations. Hot surfaces inside turbines, smoldering insulation in cable tunnels, leaking fuel in auxiliary systems, or sparks within electrical cabinets can ignite without immediate visibility.
Coal-fired units face risks from dust accumulation and conveyor systems, while gas-fired plants must monitor for leaks around compressors, valves, and burners. Steam plants deal with high-temperature surfaces and lubrication systems.
Regardless of the fuel type, the earliest warning signs — flame flicker, gas concentration buildup, smoldering materials, or heat anomalies — must be caught before they reach critical levels.
What power-plant detection systems must deliver
Fire and gas detection in power plants must withstand harsh operating conditions. Equipment is frequently exposed to high temperatures, vibrations, dust or exhaust particles, outdoor weather, and electromagnetic interference.
Sensors must react instantly to ignition, maintain accuracy over long distances, and avoid false alarms caused by ambient lighting or process heat. Detection should seamlessly integrate into turbine protection systems, fuel-isolation valves, and emergency shutdown protocols.
Additional Resources
Articles
Trusted Half a Century and How OmniGuard Leads Flame and Gas Detection Innovation >
From Hangars to Hydrogen and OmniGuard’s Expertise in High Stakes Environments >
Meet the Models and Choosing Between OmniGuard’s 660 760 and 860 Flame Detectors >
Precision Tested and How OmniGuard’s 540 545 Test Sources Ensure Detector Reliability >